Introducing the new Raspberry Pi Zero ‘W’
You all might be familiar with Raspberry Pi; the mini computer that changed the world of hobbyist and hackers. On 26 November 2015, the Raspberry Pi Zero, was launched at US $5. On 28th February 2017 a…
You all might be familiar with Raspberry Pi; the mini computer that changed the world of hobbyist and hackers. On 26 November 2015, the Raspberry Pi Zero, was launched at US $5. On 28th February 2017 a new variant of Pi Zero – The Raspberry Pi Zero W with WiFi and Bluetooth via chip scale antennas was launched. This is now the cheapest Pi with wireless network connectivity. So what makes the Raspberry Pi Zero W such a big deal?
The Raspberry Pi Zero is half the size of a Model A+, with twice the
utility. A tiny Raspberry Pi that’s affordable enough for any project. The only problem is that, in order to connect the device to network, you will either need an external USB WiFi adapter or USB to Ethernet adapter.
Raspberry Pi Zero W
Raspberry Pi Zero W Specs
- 1GHz, Single-core CPU
- 512MB RAM
- Mini-HDMI port
- Micro-USB OTG port
- Micro-USB power
- HAT-compatible 40-pin header
- Composite video and reset headers
- CSI camera connector (v1.3 only)
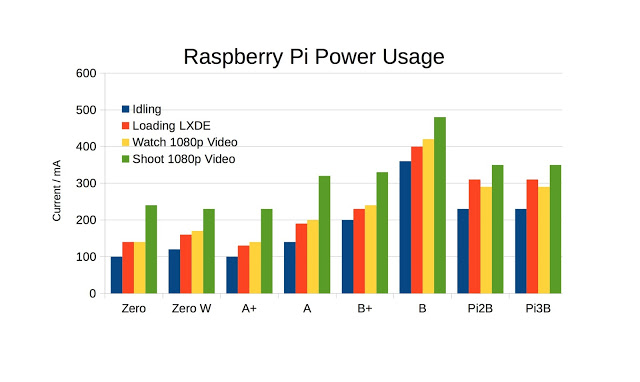
One of the major benefits of using one of the two models of Raspberry Pi Zero, including the new wireless model, is the lack of power consumption. This is handy for mobile projects where you’re running off a battery. The addition of Wi-Fi draws a little extra power.







It is very interesting topic you’ve written here . The truth I’m not related to this, but I think is a good opportunity to learn more about, And as well talk about a different topic to which I used to talk with others