RADIUS Server Secure WiFi Explained
You all will be familiar with wifi networks. Many of you will be having one in your home or your office. 90% of total WIFI networks are either WEP, WPA or WPA2 (PSK), of which WPA and…
If u are looking for something that is reliable and secure, a RADIUS server is what you need.
In most networks, normally there will be a passphrase and this passphrase will be given to everyone who wants to join the network. Simple. But the main drawback here is, there is a single preshared key for everyone. what if you dont want someone to be on your network anymore? You will have to change the passphrase and tell the new passphrase to every one else.RADIUS stands for Remote Authentication Dial In User Service.
In a RADIUS server, otherwise known as WPA WPA2 Enterprise, each user will be provided with a seperate usernames and authentication keys which can be used to login to the network and create seperate encryption keys and user sessions.
So How Does it Works
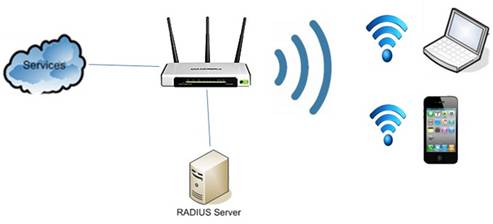
There are mainly 3 components in the WPA/WPA 2 Enterprise Wireless network
1. The Supplicant: The Supplicant is any device – laptop or mobile phones that needs access to the network
2. NAS : Network Access Server that acts as a gateway to the RADIUS server and control access to the network. It is also known as RADIUS CLEITN
3. The RADIUS Server : A RADIUS server utilizes a central database to authenticate remote users. RADIUS functions as a client-server protocol, authenticating each user with a unique encryption key when access is granted.
So what actually happen is a bit complex but I will try to explain as simple as possible. In a nutshell,
- The supplicant (mobile phone or laptop) initiates and sends a connection request to the Network Access Server (NAS).
- The Network Access Server then asks either a username and password pair or a challenge (CHAP) to the Supplicant.
- The Supplicant respond with a username and a password.
- On receiving the supplicants reply, the NAS sends the username and the uniquely encrypted password to the RADIUS server.
- The RADIUS server grants or rejects access to the Supplicant.






Hi there, Can I download this post photograph and employ it on my personal blogging site?