[WARNING] Are you using the Safest WiFi Security? WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3, WPS Difference Explained
As you all know Wi-Fi is very common these days. Whether it is in your home or your office, cafes or airports there is always Wi-Fi. When you register for a new internet connection, most Internet service providers give a free Wi-Fi router. You might have seen in hotels and restaurants there will be a paste of a piece of paper with Wi-Fi name and password or even barcode using which the guest can connect to the Wi-Fi network and enjoy free internet. That’s really convenient, right? We don’t have to pay for the internet as long as we’re their guest. But think again. Do you really think it is a good idea to connect your personal device to a public Wi-Fi network? In this post, I will be explaining the differences between WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3, and WPS and which is the best WiFi Security to protect your WiFi network from hackers.
Connecting to WiFi Network
Everything starts when you connect your mobile device or your computer to the Wi-Fi network. you might be familiar with this. How do you connect your device to the Wi-Fi network?
You will turn on mobile WiFi, scan for all the nearby Wi-Fi networks, and tap on the one you need to connect to. It will prompt for the password. You simply enter the password and hit connect. Sometimes you can simply scan the barcode and the phone will automatically connect to the Wi-Fi network. And sometimes you won’t even have to provide any password; it will automatically connect to it when you simply select the Wi-Fi name. What is actually going on in the background?
Everything is out there in thin Air
Everything on the internet as well as your WiFi network is transmitted as data packets. In the WiFi network, the data packets are transmitted to and from the router in the form of electromagnetic signals. That means any device with an antenna that is tuned to that particular frequency WiFi routers are using, can easily trap those signals. That means, everything you do, everything you send and receive, including your social media login credentials, bank transactions etc are all out there in thin air.
Sounds scary? Not really. The real question is whether these data packets are understandable to someone (a third party) who is listening to these data packets. I mean, there is no point in reading a French magazine if you don’t know French right?
WiFi Encryption
That’s where encryption comes into play. Encryption is the process of scrambling the data using a special method before the data is being sent to the receiver. This scramble data can only be unscrambled by the receiver who knows the special method which is used to scramble the data in the first place. This unscrambling process is known as decryption and the special method is called encryption key.
So how does it protect the data? Even if someone with a special antenna can capture the data packets that are sent by the receiver he won’t be able to make sense out of it since he doesn’t have the key. Please note that this process is only as strong as the encryption key as well as the algorithm that is used in the process.
WiFi Security – WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPA3 Differences
In the past few decades, wireless security engineers severed opted for various security standards to protect Wi-Fi networks and data packets from malicious actors.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
Wired Equivalent Privacy is one of the first encryption protocols that was put in place For Wi-Fi data packet encryption to prevent wireless attacks. In WEP, the same key is used to encrypt the data packets of all the WiFi devices. That means everyone had the same key.
Is WEP Secure?
This Wi-Fi security had so many vulnerabilities that made it unusable. The key that was used to encrypt the data packets was initially 64 bits Which were very very low and so it was later changed to 128 bits.
Why Is WEP not Secure?
There is something called the initialization vector or IV (works a little bit like salting during hashing) that is used as a part of the key for additional security. This initialization vector was 40 bit and it will be different for different packets. IV and WPS Key are passed through RC4 Encryption Algorithm, to form the above-mentioned 64 bit (or 128 Bi) Keystream. This 64 Bit or 128 Bit keystream is then XOR-ed with Data and CRC. This data is again concatenated with IV again (in plain text) so that the receiver can reverse the process and get the data back.
You see the problem right? The IV size is very small and will be repeated. Attackers can generate a large volume of junk traffic to collect needed packets to determine the encryption key rendering WEP useless.
WPA – WiFi Protected Access (Personal)
WPA was introduced to solve the problems of WEP and is far better than WEP. WPA uses strong protection by employing a stronger algorithm called TKIP or Temporal Key Integrity Protocol. This dynamically changes the Key while it’s being used. But still, it couldn’t live up to the mark as TKIP also had some vulnerabilities. So WPA was thrown away.
WPA2 – WiFi Protected Access 2 (Personal)
WPA2 provides a much more robust encryption and protection when compared to WPA by employing a better encryption mechanism called AES or Advanced Encryption Standard. AES uses a Symmetric Encryption algorithm which makes it strong enough to prevent brute force attacks to a great extent.
Both WPA and WPA2 Personal use a PSK-based authentication mechanism. PSK stands for Preshared Key. In PSK authentication, both Client and Access point will be having a Preshared Key which will be used for the further encryption process. This is how an Access point or router Authenticates a Client Device.
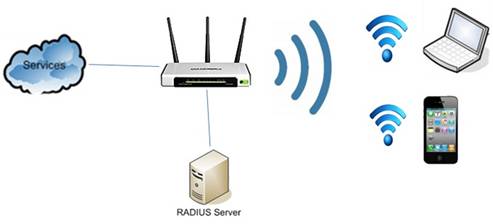
What is WPA and WPA 2 Enterprise?
In WPA and WPA2 enterprise, the authentication mechanism used is different. Here, they use a mechanism called EAP or Extensible Authentication protocol. This one uses an additional component called Authentication Server for authenticating users to use the WiFi network connectivity.
4 Way Handshake Is the process of deriving an encryption key that can be used to encrypt data using a simple key material. Depending on WPA or WPA2, there will be a handshake process that derives the encryption key that will be used to encrypt the data that will be transmitted between them.
WPA 3 WiFi Protected Access 3 – Next Generation WiFi Security
WPA 3 makes WiFi connections more secure than ever! WPA3 implements state-of-the-art security protocols for wireless connectivity infrastructures. This provides more robust authentication and a higher cryptographic strength that makes it harder to crack.
This uses 128 Bit encryption in WPA3 Personal and 192 Bit encryption in WPA3 Enterprise. In addition to the strong encryption algorithm, WPA3 provides a second line of defense for people who uses weak passwords in their WiFi network. It also protects WiFi networks from password guessing attacks and secure data even if the password is compromised. WPA3 even has the capability of protecting your data in open networks.
WPA3 Authentication
SAE or Simultaneous Authentication of Equals replaces the less-secure PSK authentication. Instead of using the PSK as the PMK, SAE arrives at a PMK, by mapping the PSK to an element of a finite cyclic group, PassWord Element (PWE), doing FCG operations on it, and exchanging it with the peer.
WPS – WiFi Protected Setup
There is another way of connecting your devices to the WiFi network. Have you ever seen a refresh icon-like button in your Router with a Label – “WPS”? All you have to do is press the WPS button in the router and then press the WPS button on the device within 120 seconds. The device will automatically connect to that WiFi router.
There is also another option to set an 8 digit pin using which you can easily connect to the WiFi network.
Although this makes it easier to connect to WiFi networks, it does have some serious flaws and disadvantages. WPS is vulnerable to brute force attacks. This means, it is very easy for an attacker to brute-force the 8 digit pin that is used for the encryption process. So, It is always safe to disable WPS in your WiFi router.
What is Open WiFi?
Open wifi is a wifi network that doesn’t require any authentication to connect. That means anyone can access the internet by simply connecting to the open wifi network without having to provide any username or password. Most of the time, these networks are unsecured which makes them vulnerable to attacks from hackers.
Why are Open WiFi Networks Dangerous?
Open wifi networks are dangerous because anyone can connect to them and use your internet connection without you even knowing about it. They don’t need any password or username, so they’re basically invisible. This is especially bad if the wifi network was created by an untrusted source like a public wifi provider in cafes or airports as these networks can be easily hacked.
How can you protect Yourself in an Open WiFi Network?
The best way to protect yourself from open wifi networks is by using a VPN service. A VPN service will encrypt all of your traffic and hide your IP address so that the hacker can’t track you down.
What is a VPN?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) allows users to connect their devices securely with an encrypted tunnel through public networks such as internet cafes, airport lounges, etc., ensuring safety & anonymity while browsing online.
How to Protect your WiFi Network?
Here are some tips you can follow to protect your WiFi network from intruders.
- Change default WiFi name and Password
- Change the Admin Panel username and password
- Disable remote management
- Enable latest wifi security features
- Hide your network from view
- Update your Router Software
- Enable Firewall
- Enable MAC Filtering
- Place the Router at the Center of the House
- Disable WPS
- Disable WiFi if you are not using it
Read more about Securing WiFi Network in this post.
Conclusion – Which is the Best WiFi Security to Protect WiFi Network from Hackers?
Short answer, definitely WPA3.
Long Answer
Wifi Security Protocols are methods to protect wifi networks from different types of cyberattacks. WEP, wifi password is the first wifi security protocol that was introduced in 1999 but it can be easily hacked because it uses a simple key for encryption which could be broken within minutes using open source tools like aircrack-ng tool. This method is also called a wifi password because it uses a string of characters as a wifi network key.
WPA was the second wifi security protocol introduced after WEP, wifi password which makes use of Message Integrity Check to make sure that data packets have not been modified in transit using an encryption algorithm like TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol). But this method also had a major flaw in TKIP that rendered it useless.
WPA2 wifi security protocol is the wifi password that was introduced in 2004 and it has a better authentication process as compared to the WPA wifi security protocol. It uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for encryption.
WPA3 wifi security protocol is the wifi password that was introduced in 2018 as a replacement for WPA and WPA2 protocols. This uses 128 Bit encryption in WPA3 Personal and 192 Bit encryption in WPA3 Enterprise for stronger wifi network protection from different types of cyberattacks like brute force attacks, dictionary attacks, etc. Another advantage of WPA 3 is it supports a stronger authentication process using Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE) instead of Preshared Key (PSK).